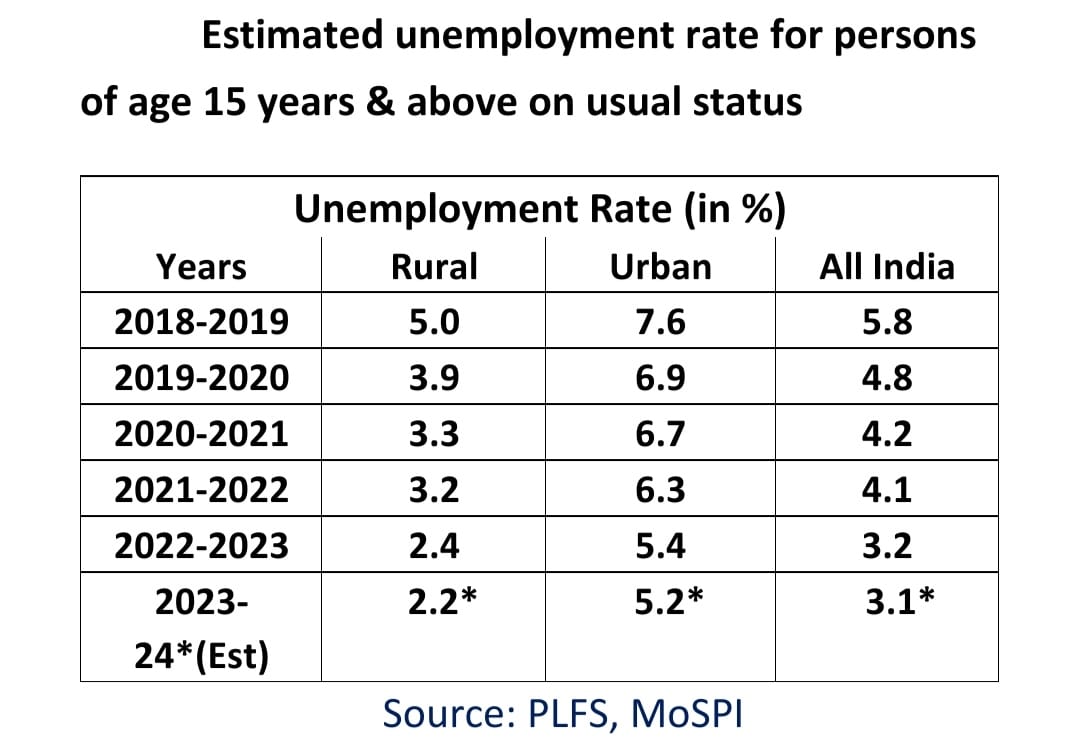
While most countries in the world, including advanced and developed economies, are experiencing a surge in unemployment rates off the back of the global economic downturn, recession, and inflation, India, under the leadership of Prime Minister Narendra Modi, has successfully steered its economy and curtailed the unemployment rate. As per the annual reports of EPFO (year-over-year) and the e-shram portal, in the last ten years, India has created an all-time record high of 19.20 crores of new salaried jobs and approximately 8.6 crores of other contract jobs through non-EPFO-registered entities and self-employment. This has made the total strength of working people between the age groups of 18 and 59 with regular jobs across the nation approximately 60.41 crores as of January 2024. As per the data available in the latest Annual PLFS Reports, the estimated unemployment rate for persons of age 15 years & above on usual status during 2018–19 to 2022–23 was as follows, and I assume it would be approximately 3.1 in FY 2023–2024.
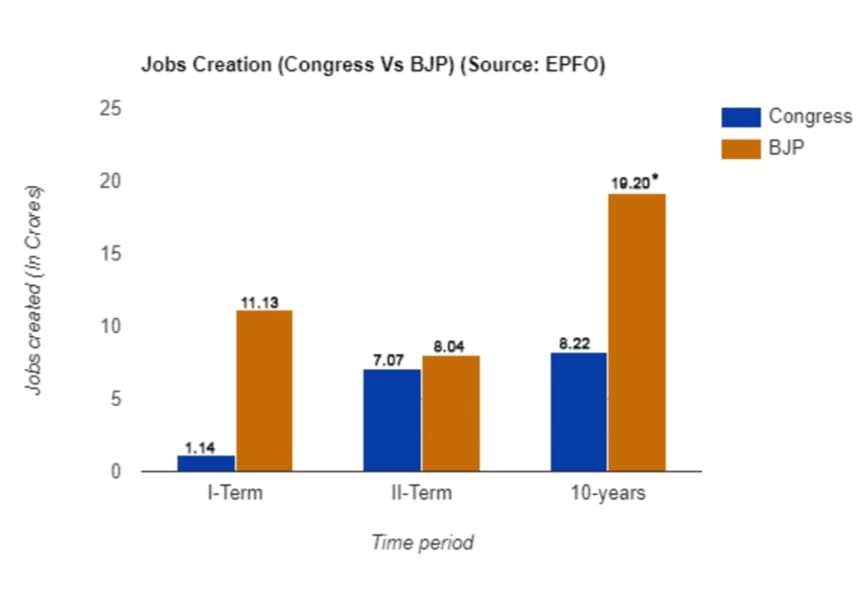
Congress-made Economic disaster (Congress VS BJP comparison)
India’s economy and employment were going down the drain between 2004 and 2014 owing to the then Congress government’s fallacious economic policies, such as disinterest in luring foreign and domestic investors, dispiriting startups and domestic entrepreneurs, cold-shouldering MSME, and omitting the use of technology. But since assuming power, the Honourable Narendra Modi has started constituting various economic policies to revive India’s economic growth. He kicked off plummeting inflation, recession, and unemployment by debuting new schemes such as Makeinindia, DigitalIndia, and other flagship programmes for promoting domestic production and exporting it. He urged the government and private sectors to make use of technology at its best. To spur on employers into creating more jobs, several constructive schemes, such as Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY), Aatmanirbhar Bharat Rojgar Yojana (ABRY), Pradhan Mantri Rojgar Protsahan Yojana (PMRPY), and PM SVANidhi were instituted. As an outcome of various economic reform measures that were taken to get rid of the Congress-made economic disaster, India has created a total of 19.20 crore new jobs between 2014 and 2024, which is 135% greater than the total of 8.22 crore jobs created between 2004 and 2014 by the then Congress Government.
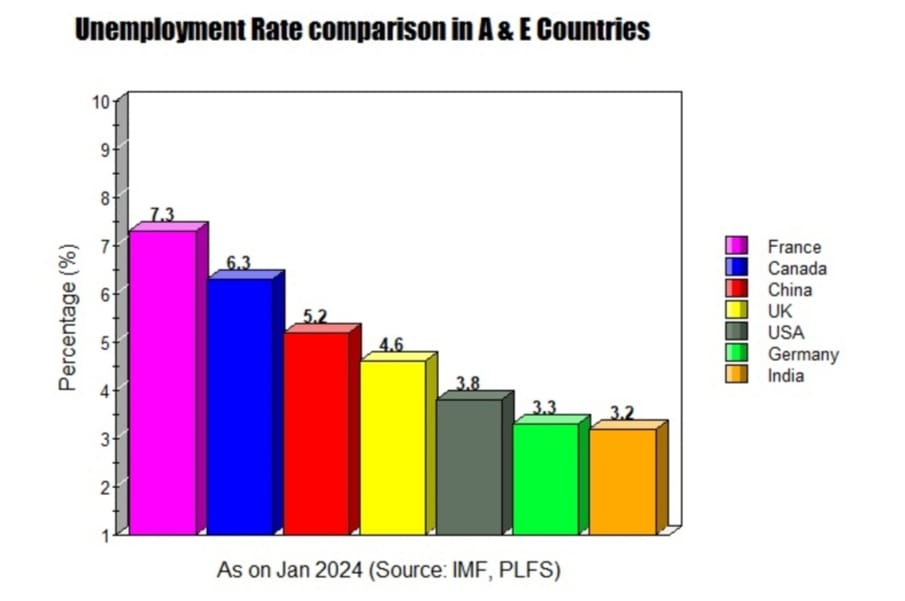
Unemployment Rate Comparison (India vs Other Countries)
On January 10, 2024, the United Nations (UN) labour agency ILO (International Labour Agency) reported that there will be a leap in the global unemployment rate (UR) between 2024 and 2025 because there has been a constant lag in creating new jobs in most of the countries post-COVID 19. The IMF has also asserted the current unemployment data for some of the advanced and emerging economies, with a forecast for the year 2025. Per IMF assessment, the current unemployment rate in the USA, Canada, and France stands at 3.8 per cent, 6.3per cent, and 7.3per cent, respectively, while Germany holds 3.3per cent and the UK has 4 per cent of UR, followed by Australia and China with 4.3 per cent and 5.2 per cent of UR, respectively. On the other hand, as per the PLFS report, India stands at 3.2 per cent of the UR currently, and the UR will decline further to approximately 3.1 per cent in 2025. India today holds the record of being one of the very few countries in the world that have created the highest number of jobs.
Employment by Capital Investments
The incumbent BJP Government has the vision that capital investment in infrastructure will have a large impact on economic growth and employment. It has incessantly been making capital investments ever since it was voted to power, and this theory has created approximately 50 lakh jobs in the unorganised sector to date. Even in the last FY 2023-2024 budget, this Government had propounded to increase capital investment outlay steeply for the 3rd year consecutively to Rs 10 lakh crores, which is 3.3 per cent of the total GDP of India. This significant increase in capital investment in recent years is indeed an endeavour by the Government to amplify economic growth and job opportunities, as they do anticipate that this will bring in approximately 75 lacs of unorganised jobs in the next couple of years.
Employment by ABRY
While the world was beholding a negative impact on the global economy owing to COVID 19 until December 2021, despite being catastrophically affected, India was focusing more on reinforcing the five vital pillars, namely economy, infrastructure, system, vibrant demography, and demand, to make the self-reliant Bharat (India) campaign a grand success. This Modi-led BJP Government had announced special Aatmanirbhar Bharat packages worth Rs 27 lakh crore. Initially, AatmaNirbhar Bharat Package 1.0 was announced on May 13, 2020. Subsequently, Package 2.0, which included the most efficient and productive scheme called Aatmanirbhar Bharat Rojgar Yojana (ABRY), was announced between October 1 and October 12 2020, followed by Package 3.0 on November 12. These comprehensive packages enticed businesses and incentivised employers to create new employment opportunities. It also lessened the layoffs and mitigated the pernicious impact of Covid 19 in MSME. As of January 20, 2024, the benefits of these packages have been provided to 60.50 lakhs of employees and 1.53 lakhs of employers. Approximately, this ABRY scheme alone created 15 lakhs of new jobs across the nation, substantially in MSME, and around 45 lakhs of employees retained their existing employment.
Employment by PMRPY
Pradhan Mantri Rojgar Protsahan Yojana (PMRPY), a 3-year visionary scheme that India had never witnessed since Independence, was initiated in August 2016 by the Ministry of Labor and Employment under the guidance of the Prime Minister to root on the EPFO-registered employers for creating more employment opportunities and bringing informal workers into the formal workforce. Under this scheme, the Union Government was paying both employee and employer contributions (i.e., 24 per cent of wages) to newly appointed employees towards their social security benefits such as EPF and EPS through EPFO for employers with up to 1000 employees and for employers with over 1000 employees, only the employee’s EPF contributions (12 per cent of wages) for an epoch of 3 years. The terminal date given for registration of new employees through employers with EPFO under this scheme was March 31, 2019, and the employers who registered until March 31, 2019, were receiving the benefits for three years from the date of registration. This scheme has created more jobs in both urban and rural areas since it incited employers to hire more workers with no financial burden. Till date, benefits have been provided to 1.23 crores of newly appointed employees through 1.52 lakh employers.
Employment by Mudra Yojana (PMMY)
Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY) was one of the dream projects of PM Modi, launched on April 8, 2015, to incentivise employers to create more employment opportunities and facilitate self-employment across the nation. Collateral-free loans up to Rs 10 lakh are being provided to unfunded micro and small business entities and individuals to enable them to set up or expand their business activities. This scheme is being seen as a jewel in the crown since it is one of the vital reasons for India’s domestic production and the creation of new jobs. Since its inception, approximately 3.1 crores of new salaried jobs and 1.5 crores of self-employed jobs have been created in both the manufacturing and service sectors, irrespective of gender. As of January 26, 2024, more than 46.78 crore loans amounting to Rs 28.05 lakh crore have been sanctioned since the launch of the scheme.
SC/ST and Women entrepreneurship
An astounding flagship programme called “Standup India “was introduced on January 16 2016, to create the oppressed class (SC/ST) and women entrepreneurs across the nation. Since the empowerment of women and the oppressed class has always been a priority for a visionary leader like PM Modi, The very objective of this scheme is to accelerate bank loans between 10 lakhs and one crore only to SC/ST and women entrepreneurs for establishing Greenfield project entities in the manufacturing, services, or trading sectors. In the event of non-individual entities, a minimum of 51 per cent of the shares or stakes should be held by either SC/ST or women entrepreneurs. As per the Standupmitra report, to date, 2.20 lakhs of SC/ST and women entrepreneurs have been given loan amounts of 49,593 crores.
SVANidhi and Vishwakarma Yojana Schemes
A couple of schemes that were exclusively designed to incentivise and aid gig workers and self-employed people were kicked off in the second term of PM Modi. Those were PM SVANidhi and PM Vishwakarma Yojana. PM SVANidhi Scheme, which is in force to date, was introduced on June 1, 2020, to accelerate collateral-free loans for street vendors to restart their businesses, which were adversely impacted during the pandemic. As of February 2024, 65.98 lakhs of vendors have been loaned under the scheme. The PM Vishwakarma Yojana was launched on September 17, 2023, to provide end-to-end support to artisans and craftspeople who work with their hands and tools (Vishwakarma) in 18 different trades across the country. This scheme aims to strengthen the quality and ensure the reach of the products and services of Vishwakarmas in the domestic and global value chains. As of February 20, 2024, 42.70 lakhs of Vishwakarmas have been verified for the benefits under the scheme.
Employment by other Flagship programmes
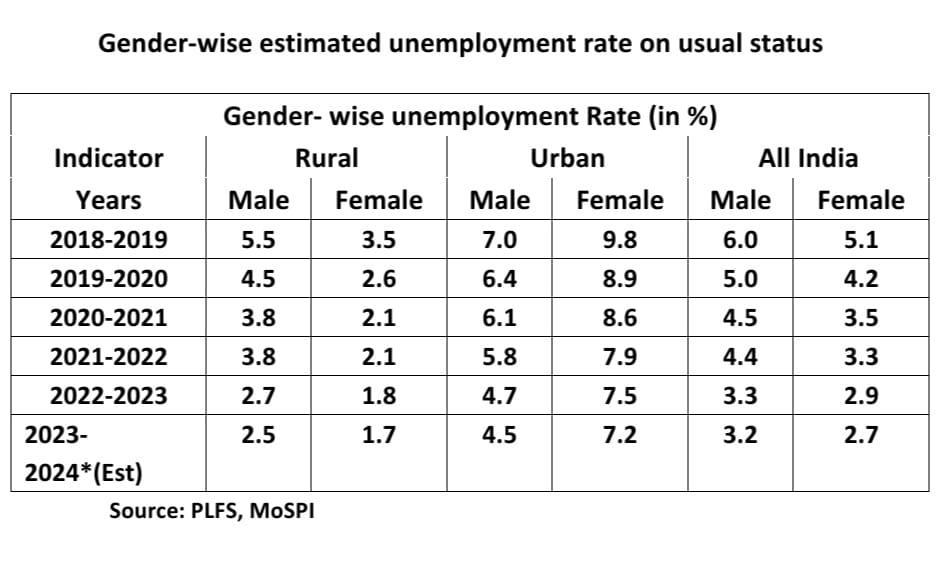
Besides many futuristic schemes that were contrived by the incumbent BJP Government to propel companies to create new salary-based job opportunities, it also instilled the thought of self-employment in the minds of youth by implementing a variety of flagship programmes promoting new young entrepreneurial talents as well. Some of the vibrant flagship programmes such as Start-up India, Make in India, Digital India, International Cooperation Scheme (ICS), Performance and Credit Rating (PCR), Marketing Assistance Scheme (MAS), Startup India Seed Fund Scheme (SISFS), Atal innovation mission (AIM) and Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes were kicked off sequentially to create more jobs for graduates and to make India a hub for the manufacturing and service sectors in the world. Other initiatives such as the Shyama Prasad Mukherji Rurban Mission (SPMRM), the Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT), Pradhan Mantri Aawas Yojna (PMAY), Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY), Pradhan MantriAwaas Yojana- Gramin (PMAY-G), Enhanced Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS) with a 20 per cent increase in the wages. PM Gati Sakthi (National Master Plan driven by seven engines, namely, Roads, Railways, Airports, Ports, Mass Transport, Waterways and Logistics) (PMGS), Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KSN), Pradhan Mantri Annadata Aay SanraksHan Abhiyan (PM-AASHA), Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY), Soil Health Card scheme (SHC), e-NAM, Agro Processing Cluster (APC), Pradhanmantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY), Silk Samagra, Weavers MUDRA Scheme (WMS), Infrastructure development and industrial corridors have created employment opportunities for male and female in both rural and urban areas. These schemes have not only aided livelihood opportunities for the rural workforce but also accorded the accessibility of both unskilled and skilled workforce in the field. A surge in the Gender employment rate can be witnessed in the column below.
Skills development for youths (Skill India Misson).
Under NSDC, various mind-boggling skill development schemes were and are being implemented by way of the Skill India Mission for youths, especially between the age groups of 15 to 25 in both rural and urban areas across the country, with the objective of increasing their proficiency for either salaried employment or self-employment.
Enhancing the skills of youth with international standards, tutoring and lending a hand through some vibrant Initiatives such as Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Grameen Kaushalya Yojana (DDU-GKY) and Rural Self Employment Training Institutes (RSETIs), National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS), Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP), National overseas Scholarship (NOS), Global engagement scheme (GES), SERB-POWER ( Fellowships & Grants) for women, Swarnjayanti Gram Swarozgar Yojana (SGSY). Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY), Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana-National Rural and Urban Livelihood Mission (DAY-NRLM) & (DAY-NULM), Skill Training & Placement (EST&P), Jan Shikshan Sansthan scheme (JSS) and Craftsman Training Scheme (CTS) , Start-up Village Entrepreneurship Programme (SVEP, Samarth (Scheme For Capacity Building In Textile Sector) have not only fostered aplomb within them but also proliferated the employability of youths in Bharat. Monetary aid is being granted to individuals or Self Help Groups (SHGs) to set up fructuous self-employment ventures or super micro entities. These schemes created a major impact on labour force participation as well as workforce availability across the country.
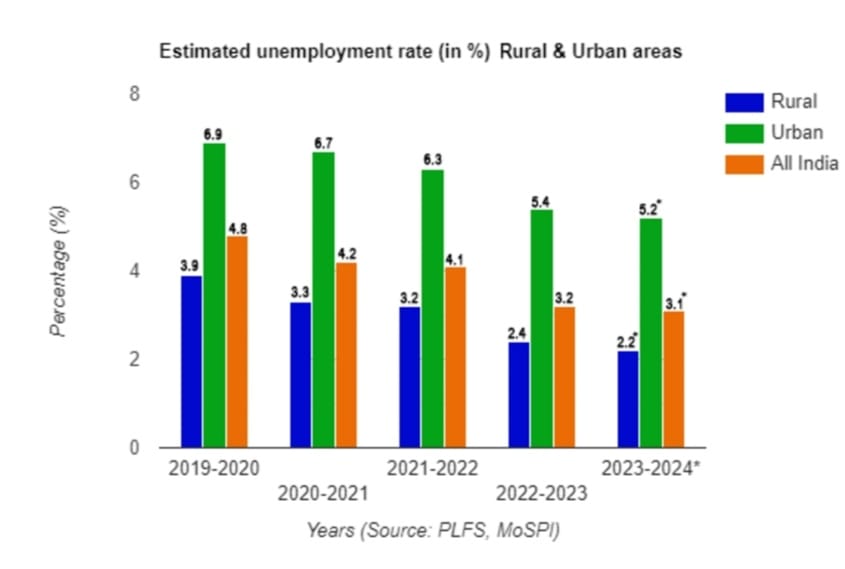
The livelihood of more than 1.98 crore Women Farmers (Mahila Kisan) is being bolstered under the Farm Livelihood intervention scheme, and more than 2.18 lakh women entrepreneurs were aided under the SVEP. Under PMKVY, as of December 31, 2023, 1.40 crores of candidates have been trained, of which 24.39 lakh candidates have been reported to be placed across the country. With these flagship programmes and skill development initiatives taken in the first tenure of Prime Minister Narendra Modi, the estimated unemployment rate in both rural and urban areas embarked to shrink in the second tenure, and this can be noticed in the bar chart below, which is carved out of the available data (except FY 2023-2024) from PLFS and MoSPI.




















Comments