Umashankar Mishra
The study assessed the tree diversity and ecosystem carbon storage through the traditional agroforestry system practised by the local communities.
New Delhi: Pineapple-based agroforestry, traditionally practised by ethnic “Hmar” tribe in southern Assam, can be a sustainable alternative to jhum cultivation for North East India. According to a new study, this traditional practice can provide twin solutions for climate change and biodiversity loss. The Department of Ecology and Environmental Science, Assam University, Silchar, with support from the Climate Change Program Division of the Department of Science & Technology (DST) carried this study out.
Researchers are looking for agroforestry options that would also offer high carbon storage potential and tree diversity to couple this with solutions for challenges of climate change and biodiversity loss, the DST statement said.
Jhum cultivation, also called swidden agriculture, the dominant agricultural practice in the region, has become unsustainable primarily due to the reduced fallow cycle resulting in depletion in soil fertility, severe soil erosion, and low agronomic productivity. Hence, North East India and many south Asian countries are shifting to agroforestry and high-value cropping systems from traditional jhum practices, which are considered sustainable and profitable alternatives over the past decades.
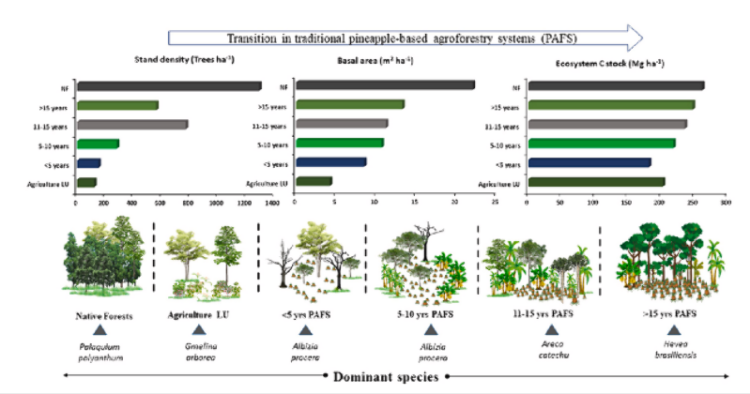
The study assessed the tree diversity and ecosystem carbon storage through the traditional agroforestry system practised by the local communities. It showed that the system they practice maintains a steady ecosystem carbon stock while reducing land-use-related carbon emission and providing additional co-benefits to the communities.
The research team, led by Arun Jyoti Nath, Associate Professor in the Department of Ecology and Environmental Science, Assam University, conducted this study in the ethnic villages in the Cachar district of Assam part of the Himalayan foothills and the Indo-Burma, centre of a global biodiversity hotspot. They explored changes in tree diversity and transition of dominant tree species from swidden agriculture through different aged PAFS. The changes in the biomass carbon and ecosystem carbon storage in tree and pineapple components from swidden
agriculture through different aged PAFS were also noted.
Researchers found that farmers apply traditional knowledge for tree selection through prior knowledge and long-term farming experience. Additionally, fruit trees such as Areca catechu and Musa species are planted on farm boundaries as live fences. The live fence reduces soil erosion and acts as a windbreak and shelterbelt. A combination of economically important trees like Albiziaprocera, Parkiatimoriana, Aquilariamalaccensis, and fruit trees like papaya, lemon, guava, litchi, and mango with pineapple caters for both home-consumption and
selling all year round. The upper canopy trees regulate light, enhance biomass inputs, and increase farm diversity, resulting in soil fertility and improved plant nutrition. The tree-related management practices promote the conservation of the farmers favoured indigenous fruit trees. In the older pineapple agroforestry farms, farmers introduce rubber trees.
The research shows that the practice can be applied for the REDD+ mechanism to add to the carbon capturing and reducing deforestation by contributing to tree cover, which may further incentivise against the carbon credit to the poor farmers.
Pineapple agroforestry systems (PAFS) are dominant land use in the Indian Eastern Himalayas and other parts of Asia and are mostly grown in association with multipurpose trees. The ethnic “Hmar” tribe in southern Assam has been cultivating pineapple for centuries. At present, they practice the indigenous PAFS for both home consumption and boosting economic benefits.
They have applied traditional knowledge to evolve a unique agroforestry system. The study published in the ‘Journal of Environmental Management’ recently can provide information about emission factors for the indigenous agro-ecosystems in North East India for mitigation purposes, facilitating the formulation of incentives for the communities. It could also equip forest managers with information for accounting for the changes in carbon storage due to deforestation and jhum cultivation.
Courtesy: India Science Wire












Comments